Insulated panel roofing offers architects a versatile, energy-efficient solution for enhancing building performance. Insulated panel roofing has become a popular choice in the construction industry with numerous advantages, such as energy efficiency, quick installation, weather resistance, fire resistance, and long lifespan. In this blog, we will explore key design considerations for architects when incorporating insulated panel roofing into their projects.
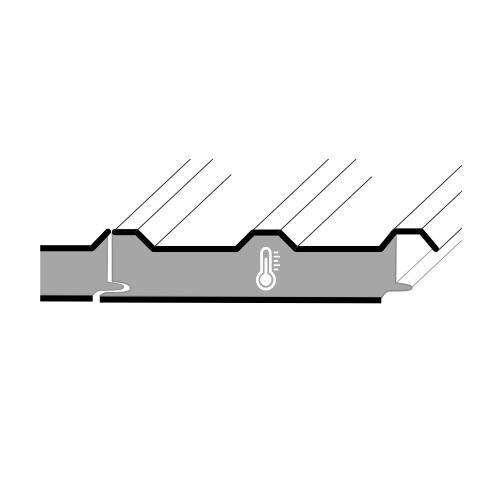
Insulated Panel roofing panels provide a cost-effective method for improving energy efficiency in buildings. These panels are made up of steel skins with a foam core inside (typically PIR or PUR foam) that provides insulation. By reducing heat transfer, they decrease heating and cooling requirements, leading to less energy consumption and lower utility expenses. Utilizing these panels can ultimately improve a building’s overall energy efficiency.
These panels offer robust support to the building structure and can be quickly assembled, leading to efficient construction processes and shorter project timelines.
The insulated roof panels are designed to be weather-sealed, providing a sturdy barrier against thermal and moisture damage caused by environmental elements over time. The sturdy construction shields the building from harsh conditions and ensures long-term performance, reducing the risk of damage from wind, rain, or snow.
One of the main advantages of insulated roof panels is their long lifespan. They can last more than 60 years, much longer than traditional roofing materials that typically last between 12 to 20 years. Many manufacturers even offer a 50-year warranty to ensure their durability and performance. So, insulated roof panels are worth considering if you’re looking for a roofing option that will last for decades and provide excellent protection for your home.
Insulated panel roofing utilizes metal roof panels made from non-combustible steel, providing excellent fire resistance. This feature plays a key role in preventing the spread of fire, thereby improving the overall safety of the building.
Investing in insulated roof panels can lead to significant cost savings in the long run. These panels not only reduce utility expenses but also require less maintenance compared to traditional options. This makes them a smart investment for any building. By opting for insulated roof panels, you can ensure maximum return on investment and enjoy financial benefits over the long term.
Insulated metal panels with a PUR core can usually attain R-values from 5 to 7.1 per inch, while others with a mineral fiber core can provide R-values from 3.6 to 4.3 per inch. These R-values signify the amount of thermal insulation that the panels provide.
The minimum pitch needed for an insulated panel roof can differ depending on factors like the design, local building codes, and the type of insulated panel utilized. To determine the correct minimum pitch for a specific insulated panel roofing system, it is crucial to review the manufacturer’s specifications and local regulations. This is necessary to ensure the roof functions optimally and has proper water drainage.
Architects can enjoy numerous advantages by using insulated panel roofing, including enhanced energy efficiency, durability, fire resistance, and cost savings. To fully leverage these benefits, it’s crucial for architects to carefully consider the key design considerations outlined above. By incorporating insulated panel roofing into their architectural designs, architects can make sustainable and practical choices that improve both the performance and aesthetics of their buildings.
